Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
柴沼 智博; 平野 宏志*; 木村 泰久; 會田 貴洋; 吉田 将冬; 永井 佑哉; 北村 哲浩
保健物理(インターネット), 58(2), p.91 - 98, 2023/08
原子力機構プルトニウム燃料技術開発センターは、簡易に組み立てられる緊急避難用グリーンハウス(GH)を開発した。本稿では本GHを開発するに至った背景について述べた後、従来の緊急避難用GHの具体的な問題点を整理し、それらをどのように改良・改善し新たなGHを開発したかを説明した。また、本GHを実際に運用することで出現した新たな問題点についても触れ、施した更なる改良・改善内容を紹介した。
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(5), p.1742 - 1756, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is a significant issue when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. After the Fukushima-Daiichi accident in Japan, we have investigated in-depth the hydrogen transport mechanisms by utilizing experimental and numerical approaches. Computational fluid dynamics is a powerful tool for better understanding the transport behavior of gas mixtures, including hydrogen. This paper describes a large-eddy simulation of gas mixing driven by a high-buoyancy flow. We focused on the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfers driven by the horizontal high-buoyant flow during density stratification. For validation, the experimental data of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility were used. With a high-power heater for the gas-injection line in the CIGMA facility, a high temperature flow of approximately 390 C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
C was injected into the test vessel. By using the CIGMA facility, we can extend the experimental data to the high temperature region. The phenomenological discussion in this paper help understand the heat and mass transfer induced by the high-buoyancy flow in the containment vessel during a severe accident.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104415_1 - 104415_16, 2022/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis and validation works from the previous experimental study on the natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of air and helium (as a mimic gas of hydrogen). The experiment was conducted in the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) facility at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The numerical simulation was carried out to analyze the detailed effect of the cooling region on the erosion of the helium stratification layer. The temporal and spatial evolution of the helium concentration and the gas temperature inside the containment vessel was predicted and validated against the experimental data. In addition, two stratification behaviors that depend on the cooling location were presented and discussed. The CFD simulation confirmed that an upper head cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-rich zone. Meanwhile, the upper half body cooling caused two counter-rotating vortexes in the helium-poor zone. These findings are important to understand the mechanism of the density stratification process driven by natural convection in the containment vessel.
石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; Hamdani, A.; 廣瀬 意育
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 168, p.108867_1 - 108867_20, 2022/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to improve computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis accuracy to estimate thermal flow in a containment vessel during a severe accident. Previous studies pointed out the importance of the influence of initial and boundary conditions on the CFD analysis. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the influence of initial and boundary conditions by numerical analysis of natural convection experiments in a large containment vessel test facility CIGMA(Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus). A density stratification layer was initially formed in the vessel using helium and air, and external cooling of the vessel surface-induced natural convection. In this study, we carried out numerical simulations of the density stratification erosion driven by the natural convection using the RANS (Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes) model. As a result, the temperature boundary condition of the small internal structure in the vessel had a significant influence on the fluid temperature distribution in the vessel. The erosion velocity of the density stratification layer changed depending on the initial gas concentration distribution. Then, appropriate settings of the temperature and gas concentration conditions are necessary for accurate analysis.
安部 諭; Hamdani, A.; 石垣 将宏*; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 166, p.108791_1 - 108791_18, 2022/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper describes an experimental investigation of natural convection driven by outer surface cooling in the presence of density stratification consisting of an air-helium gas mixture (as mimic gas of hydrogen) in an enclosed vessel. The unique cooling system of the Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus (whose test vessel is a cylinder with 2.5-m diameter and 11-m height) is used, and findings reveal that the cooling location relative to the stratification plays an important role in determining the interaction behavior of the heat and mass transfer in the enclosed vessel. When the cooling region is narrower than the stratification thickness, the density-stratified region expands to the lower part while decreasing in concentration (stratification dissolution). When the cooling region is wider than the stratification thickness, the stratification is gradually eroded from the bottom with decreasing layer thickness (stratification breakup). This knowledge is useful for understanding the interaction behavior of heat and mass transfer during severe accidents in nuclear power plants.
安部 諭; Studer, E.*; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 368, p.110785_1 - 110785_14, 2020/11
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The hydrogen behavior in a nuclear containment vessel is one of the significant issues raised when discussing the potential of hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool for better understanding the turbulence transport behavior of a gas mixture, including hydrogen. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) is a practical-use approach for simulating the averaged gaseous behavior in a large and complicated geometry, such as a nuclear containment vessel; however, some improvements are required. We implemented the dynamic modeling for  based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
based on the previous studies into the OpenFOAM ver 2.3.1 package. The experimental data obtained by using a small scale test apparatus at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was used to validate the RANS methodology. Moreover, Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) was performed to phenomenologically discuss the interaction behavior. The comparison study indicated that the turbulence production ratio by shear stress and buoyancy force predicted by the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for
was a better agreement with the LES result, and the gradual decay of the turbulence fluctuation in the stratification was predicted accurately. The time transient of the helium molar fraction in the case with the dynamic modeling was very closed to the VIMES experimental data. The improvement on the RANS accuracy was produced by the accurate prediction of the turbulent mixing region, which was explained with the turbulent helium mass flux in the interaction region. Moreover, the parametric study on the jet velocity indicates the good performance of the RANS with the dynamic modeling for  on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for
on the slower erosive process. This study concludes that the dynamic modeling for  is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
is a useful and practical approach to improve the prediction accuracy.
Hamdani, A.; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.5463 - 5479, 2019/08
The present study introduces thermal mixing and stratification produced by heated air jet located at the bottom level of the containment vessel. The investigation was carried out experimentally and numerically in the large containment vessel called CIGMA (Containment InteGral effects Measurement Apparatus). The experiments were conducted with external surface cooling and various air jet inlet temperatures. The containment cooling was done by flooding the water on the external side of half-upper of a vessel. To identify their influence on the thermal mixing and stratification phenomena, the investigation focuses on mixing convection which occurred in the cooled region of a containment vessel. Temperature distribution and jet velocity were measured by thermocouple and Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) respectively. Numerical simulation was performed using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) code OpenFOAM to investigate the detail effects of external cooling on the fluid flow and thermal characteristics in the test vessel. CFD results showed a good agreement with experimental data on both temperature and velocity. Both temperature and velocity of hot air jet decayed rapidly downstream jet nozzle. Thermal stratification was observed by visualization of temperature contour maps over a cross-section in the containment vessel. Vigorous mixing was also noticed in the upper region of the containment vessel. Effect of external cooling on mixing and the thermal stratification were presented and discussed.
伊藤 主税; 内藤 裕之; 石川 高史; 伊藤 敬輔; 若井田 育夫
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所の原子炉圧力容器と格納容器の内部調査への適用を想定して、光ファイバーの耐放射線性を向上させた。原子炉圧力容器内の線量率として想定されている~1kGy/hレベルの放射線環境に適用できるよう、OH基を1000ppm含有した溶融石英コアとフッ素を4%含有した溶融石英クラッドからなるイメージ用光ファイバを開発し、光ファイバをリモートイメージング技術に応用することを試みた。イメージファイバの本数は先行研究時の2000本から実用レベルの22000本に増加させた。1MGyのガンマ線照射試験を行った結果、赤外線画像の透過率は照射による影響を受けず、視野範囲の空間分解能の変化も見られなかった。これらの結果、耐放射線性を向上させたイメージファイバを用いたプロービングシステムの適用性が確認できた。
安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2018/10
At Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), small scale experiment, named VIMES (VIsualization and MEasurement system on stratification behavior) experiment, has been performed since 2014. In this paper, we introduce the influence of grating type obstacle to the VIMES experiment. Two types of grating obstacle were constructed based on the aperture area ratio. The obstacles were placed at the intermediate position between the jet nozzle exit and bottom of the initial stratification. Experimental results showed that the vertical jet was strongly affected by the grating obstacle. Due to the rectifying effect, the radial spreading was suppressed and the velocity magnitude on the jet center line became larger than that in case without the grating obstacle. Meanwhile, due to the resistance effect, the integral momentum flux of the vertical jet was decayed with decrease of the aperture area ratio. It means that in case with the grating obstacle the integral jet penetration strength was decayed, although the local jet penetration to the stratification was stronger than that in case without the grating obstacle. Also, the slower stratification breakup could be observed with decrease of the aperture area ratio, indicating that stratification breakup rate to be discussed in detail considering every possible effect of a jet penetration.
安部 諭; Studer, E.*; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 331, p.162 - 175, 2018/05
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:91.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)Density stratification and its breakup are important phenomena to consider in the analysis of the hydrogen distribution during a severe accident. Many previous experimental studies, using helium as mimic gas of hydrogen, focused on the stratification breakup by a vertical or horizontal jet. However, in a real containment vessel, the upward flow pattern can be considered diffuse and buoyant neither pure jet nor pure plume. HM1-1 and HM1-1bis tests in the MISTRA facility were performed to investigate such erosive flow pattern created from a horizontal hot air jet impinging on a vertical cylinder. The experimental results indicated that the jet flow was quickly mixed with the surrounding gas in the lower region of the initial stratification, and deaccelerated by buoyancy force therein. Consequently, the erosive process became slower at the upper region of the initial stratification. Those observed behavior was analyzed using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques focusing on models for turbulent Schmidt and Prndtl numbers. Some previous studies mentioned that these numbers significantly change in the stratified flow. The changes of  and
and 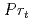 are very important factor to predict the stratification erosion process. The results have indicated that the simulation can be much improved by using appropriate dynamic models for those numbers. This research is a collaboration activity between CEA and JAEA.
are very important factor to predict the stratification erosion process. The results have indicated that the simulation can be much improved by using appropriate dynamic models for those numbers. This research is a collaboration activity between CEA and JAEA.
柴本 泰照; 石垣 将宏; 安部 諭; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 14 Pages, 2017/09
The present paper introduces the recent outcome from the CIGMA experiments regarding containment vessel cooling, in which an external side of a vessel upper head was flooded by water. The test vessel was initially pressurized by steam and noncondensable gas (air and/or helium), and was subsequently cooled by pouring water to the outside of the vessel top. Similar experiments were performed by authors using air-steam binary system in the previous study, which showed several characteristic phenomena such as inverse temperature stratification. The experimental conditions were extended systematically in this study to investigate the effects of initial gas composition and distribution in a vessel. The measurement results indicated that natural circulation was significantly affected by distributions of each gas species. In particular, it was enhanced when the gas density became heavier after condensation on the vessel inner wall, while it was suppressed when the gas density became lighter, creating density stratification with helium-rich gas in the upper region. The results are explained by the simplified model.
市川 正一; 千葉 悠介; 大野 史靖; 羽鳥 雅一; 小林 孝典; 上倉 亮一; 走利 信男*; 犬塚 泰輔*; 北野 寛*; 阿部 恒*
JAEA-Research 2017-001, 40 Pages, 2017/03
日本原子力研究開発機構は、高速増殖原型炉もんじゅのプラント工程への影響を低減するため、現在、原子炉格納容器全体漏えい率試験で用いている塩化リチウム式露点検出器の代替品として、静電容量式露点検出器の検証試験を実施した。原子炉格納容器全体漏えい率試験(試験条件: 窒素雰囲気、24時間)における静電容量式露点検出器の測定結果は、既存の塩化リチウム式検出器と比較して有意な差は無かった。また、長期検証試験(試験条件:空気雰囲気、2年間)においては、静電容量式露点検出器は、高精度鏡面式露点検出器との比較の結果、「電気技術規程(原子力編)」の「原子炉格納容器の漏えい試験規定」に基づく使用前検査時に要求される機器精度(精度: 2.04
2.04 C)を長期間にわたり有することを確認した。
C)を長期間にわたり有することを確認した。
Zheng, X.; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 49(2), p.434 - 441, 2017/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)Containment venting is one of essential measures to protect the integrity of the final barrier of a nuclear reactor during severe accidents, by which the uncontrollable release of fission products can be avoided. The authors seek to develop an optimization approach, from a simulation-based perspective, to the venting operations by using an integrated severe accident code, THALES2/KICHE. The effectiveness of containment venting strategies needs to be verified via numerical simulations based on various settings of venting conditions. The number of iterations, however, needs to be controlled for cumbersome computational burden of integrated codes. Bayesian optimization is an efficient global optimization approach. By using Gaussian process regression, a surrogate model of the "black-box" code is constructed. It can be updated simultaneously whenever new simulation results are acquired. With predictions via the surrogate model, upcoming locations of the most probable optimum can be revealed. The sampling procedure is adaptive. The number of code queries is largely reduced for the optimum finding, compared with pure random searches. One typical severe accident scenario of a boiling water reactor is chosen as an example. The research demonstrates the applicability of the Bayesian optimization approach to the design and establishment of containment-venting strategies during severe accidents.
柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介; 石垣 将宏; 安部 諭
Proceedings of 11th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-11) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) initiated the ROSA-SA project in 2013 for the purpose of studying thermal hydraulics relevant to over-temperature containment damage, hydrogen risk, and fission product transport. For this purpose, the JAEA newly constructed the Containment InteGral Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) in 2015 for the experiments addressing containment responses, separate effects, and accident managements. Recently, we successfully conducted first experiments using CIGMA to characterize the facility under typical experimental conditions. Among these experiments, the present paper focuses on the results of containment cooling tests, for which an upper part of the vessel outer surface was cooled by spray water. Several distinctive phenomena were observed in the tests, including inverse temperature stratification in the vessel due to the cooling in the upper region. The RELAP5 analysis result was also presented to roughly indicate the prediction capability of the best-estimate two-phase flow code in predicting the containment thermal hydraulics.
Zheng, X.; 石川 淳; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
Containment venting is one of essential measures to protect the integrity of the final barrier of a nuclear reactor, by which the uncontrollable release of fission products can be avoided. The authors seek to develop an optimization approach to the planning of containment-venting operations by using THALES2/KICHE. Factors that control the activation of the venting system, for example, containment pressure, amount of fission products within the containment and pH value in the suppression chamber water pool, will affect radiological consequences. The effectiveness of containment venting strategies needs to be confirmed through numerical simulations. The number of iterations, however, needs to be controlled for cumbersome computational burden of severe accident codes. Bayesian optimization is a computationally efficient global optimization approach to find desired solutions. With the use of Gaussian process regression, a surrogate model of the "black-box" code is constructed. According to the predictions through the surrogate model, the upcoming location of the most probable optimum can be revealed. The number of code queries is largely reduced for the optimum finding, compared with simpler methods such as pure random search. The research demonstrates the applicability of the Bayesian optimization approach to the design and establishment of containment-venting strategies under BWR severe accident conditions.
柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介; 堀田 亮年*
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 58(9), p.553 - 557, 2016/09
, 58(9), p.553 - 557, 2016/09
日本原子力研究開発機構安全研究センターでは、シビアアクシデント対策の強化を特徴とする新しい安全規制を支援するため、2013年にROSA-SA計画を開始し、今般、本計画の中核となる大型格納容器実験装置CIGMA(Containment InteGral Measurement Apparatus)を完成させた。CIGMAは、設計温度や計測点密度において世界有数の性能を有しており、シビアアクシデント時の格納容器内の事故進展挙動や事故拡大防止に係る熱水力実験を実施することができる。本稿では、本計画と既往研究の概要を述べるとともに、CIGMA装置の特徴、及びこれまで実施した一連の実験結果を紹介する。
柴本 泰照; 安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 与能本 泰介
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2016/06
There has been an extensive reorientation of the light water reactor research in Japan since the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station accident, which focuses on severe accidents and accident managements. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) initiated the ROSA-SA project in 2013 for the purpose of studying thermal hydraulics relevant to over-temperature containment damage, hydrogen risk, and fission product transport. For this purpose, the JAEA newly constructed the Containment InteGral Measurement Apparatus (CIGMA) in 2015 for the experiments addressing containment responses, separate effects, and accident managements. Recently, we successfully conducted first experiments using CIGMA to characterize the facility under typical experimental conditions investigating basic phenomena such as buildup of pressure by steam injection, containment cooling and depressurization by internal or external cooling, and density stratified layer mixing by impinging jet. This paper provides an overview of the research programs, the brief description of the facility specification and the outcomes obtained from the first experiments.
Mascari, F.*; 中村 秀夫; Umminger, K.*; De Rosa, F.*; D'Auria, F.*
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.4921 - 4934, 2015/08
The phenomenological analyses and thermal hydraulic characterization of a nuclear reactor are the basis for its design and safety evaluation. Scaled down tests of Integral Effect Test (IET) and Separate Effect Test (SET) are feasible to develop database. Though several scaling methods such as Power/Volume, Three level scaling and H2TS have been developed and applied to the IET and SET design, direct extrapolation of the data to prototype is in general difficult due to unavoidable scaling distortions. Constraints in construction and funding for test facility demand that a scaling compromise is inevitable further. Scaling approaches such as preservation of time, pressure and power etc. have to be adopted in the facility design. This paper analyzes some IET scaling approaches, starting from a brief analysis of the main characteristics of IETs and SETFs. Scaling approaches and their constraints in ROSA-III, FIST and PIPER-ONE facility are used to analyze their impact to the experimental prediction in Small Break LOCA counterpart tests. The liquid level behavior in the core are discussed for facility scaling-up limits.
与能本 泰介; 柴本 泰照; 竹田 武司; 佐藤 聡; 石垣 将宏; 安部 諭; 岡垣 百合亜; 孫 昊旻; 栃尾 大輔
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.5341 - 5352, 2015/08
This paper summarizes thermal-hydraulic (T/H) safety studies being conducted at JAEA based on the consideration of research issues after the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Station accident. New researches have been initiated after the accident, which are related to containment thermal hydraulics and accident management (AM) measures for the prevention of core damage under severe multiple failure conditions. They are conducted in parallel with those initiated before the accident such as a research on scaling and uncertainty of the T/H phenomena which are important for the code validation. Those experimental studies are to obtain better understandings on the phenomena and establish databases for the validation of both lumped parameter (LP) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) codes. The research project on containment thermal hydraulics is called the ROSA-SA project and investigates phenomena related to over-temperature containment damage, hydrogen risk and fission product (FP) transport. For this project, we have designed a large-scale containment vessel test facility called CIGMA (Containment InteGral Measurement Apparatus), which is characterized by the capability of conducting high-temperature experiments as well as those on hydrogen risk with CFD-grade instrumentation of high space resolution. This paper describes the plans for those researches and results obtained so far.
安部 諭; 石垣 将宏; 柴本 泰照; 与能本 泰介
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, 9(7), p.599 - 607, 2015/07
格納容器内での多成分ガスで形成される密度成層を精度よく解析することはシビアアクシデントの安全評価の上で重要である。日本原子力研究開発機構は格納容器内熱水力現象調査を目的としてROSA-SAプロジェクトを開始した。このプロジェクトの一環として、我々は浮力ジェットによる密度成層の侵食および崩壊についれ数値流体力学(CFD)解析を実行した。その解析では、既往研究でよく使われているが密度成層の侵食・崩壊を過大予測するRANS解析の改善を試みた。具体的には、低Re型k- モデルをベースとして、ジェットの成層への貫入部分での乱流エネルギーを適切に評価、密度成層内での乱流抑制効果を再現するための改良をほどこした。RANS解析の結果は、計算コストは莫大になるものの精度が高いとされるLES解析と比較をおこなった。その結果、密度成層の侵食・崩壊について、本研究で適用した改良型のモデルは従来モデルよりもLES解析とのよく一致した。
モデルをベースとして、ジェットの成層への貫入部分での乱流エネルギーを適切に評価、密度成層内での乱流抑制効果を再現するための改良をほどこした。RANS解析の結果は、計算コストは莫大になるものの精度が高いとされるLES解析と比較をおこなった。その結果、密度成層の侵食・崩壊について、本研究で適用した改良型のモデルは従来モデルよりもLES解析とのよく一致した。